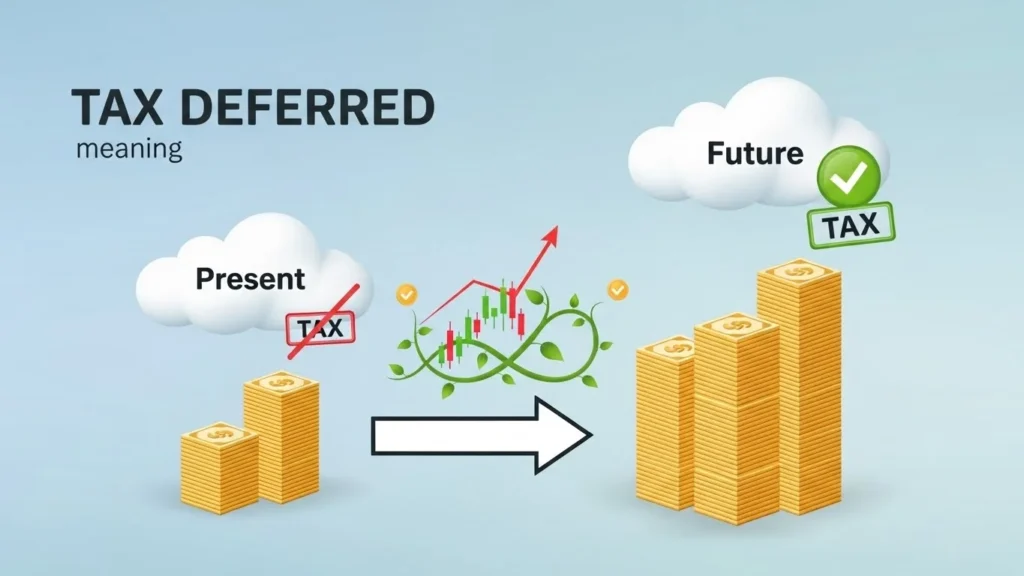
You may have seen the term tax deferred while reading about investments, retirement plans, or savings accounts and felt confused. Many people think tax-deferred means tax-free, but that’s not true.
Understanding the tax deferred meaning is important because it affects how much money you keep today and how much you may owe later. Updated for 2026, this guide explains tax-deferred income in clear, beginner-friendly language with practical examples.
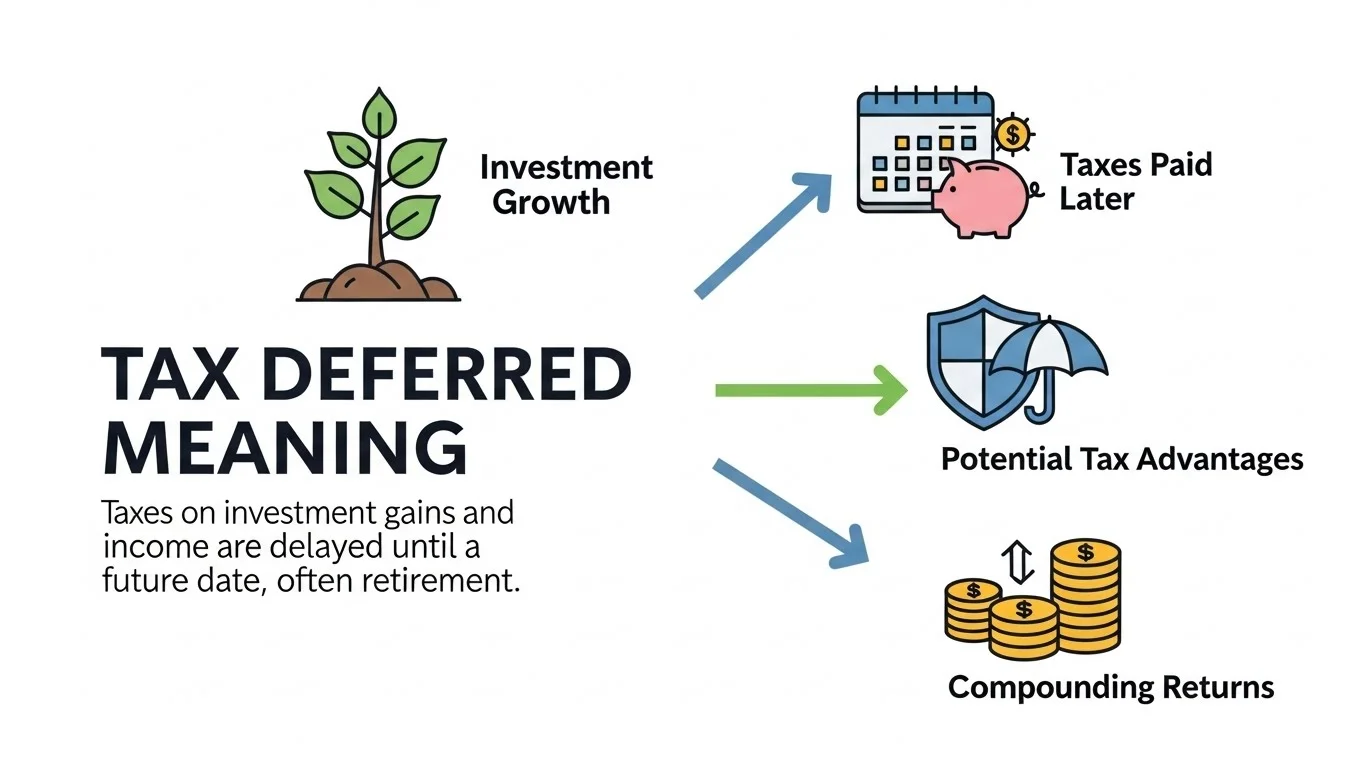
What Does Tax Deferred Mean?
Tax deferred means you do not pay taxes right now, but you will pay them later in the future.
In simple words:
Tax deferred means taxes are postponed, not canceled.
You are delaying the tax payment until a later time, often when you withdraw money.
How Tax Deferral Works
Tax deferral works by shifting the tax obligation to the future.
Here’s the basic process:
You earn or invest money
Taxes are not taken immediately
The money grows over time
You pay taxes when you withdraw or use the money
This delay can allow your money to grow faster.
Tax Deferred vs Tax Free: Key Difference
Many people confuse these two terms.
Tax deferred: Taxes are paid later
Tax free: Taxes are never paid
Example:
A retirement account may be tax deferred, meaning withdrawals are taxed later.
Some accounts are tax free, meaning withdrawals are not taxed at all.
Understanding this difference prevents costly mistakes.
Common Examples of Tax-Deferred Accounts
Tax-deferred options are common in financial planning.
Examples include:
Retirement savings plans
Pension plans
Certain investment accounts
Employer-sponsored savings programs
In these cases, taxes are delayed until retirement or withdrawal.
Tax Deferred Meaning in Investments
In investing, tax deferred allows earnings to grow without immediate tax deductions.
Benefits include:
More money staying invested
Compounding growth
Potentially lower tax rate in the future
However, taxes will apply when money is withdrawn.
Tax Deferred Meaning in Retirement Planning
Tax deferral is especially popular in retirement planning.
Why people choose it:
Income may be lower after retirement
Lower tax rate later
Long-term growth benefits
This strategy helps manage taxes across different life stages.
Advantages of Tax Deferred Income
Tax deferral offers several benefits.
Key advantages:
Immediate tax savings
Faster growth potential
Better cash flow today
Useful for long-term planning
For many people, delaying taxes makes financial sense.
Disadvantages of Tax Deferred Income
Tax deferral also has downsides.
Possible drawbacks:
Taxes are unavoidable later
Future tax rates may be higher
Required withdrawals may apply
Less flexibility with withdrawals
It’s important to plan ahead.
When Paying Taxes Later Can Be Helpful
Tax deferral is often helpful when:
You expect lower income in the future
You are saving for retirement
You want long-term investment growth
It may not be ideal for short-term savings.
Common Mistakes and Misunderstandings
People often misunderstand tax deferred because:
They think it means tax-free
They forget future tax obligations
They ignore withdrawal rules
They underestimate future tax rates
Clear understanding helps avoid surprises.
Tax Deferred Meaning in Simple Everyday Terms
Think of tax deferral like borrowing time.
You’re saying:
“I’ll pay taxes later, not today.”
The money works for you now, but the tax bill eventually arrives.
Related Financial Terms
Terms often related to tax deferred include:
Taxable income
Capital gains
Tax-free income
Retirement savings
Withdrawals
Learning these terms makes financial decisions easier.
FAQs
What does tax deferred mean in simple words?
It means you delay paying taxes until a later time.
Is tax deferred the same as tax free?
No. Tax deferred means you pay taxes later; tax free means you don’t pay them at all.
Why do people choose tax-deferred accounts?
To save taxes now and allow money to grow over time.
When do you pay taxes on tax-deferred money?
Usually when you withdraw or use the money.
Is tax deferral good for everyone?
Not always. It depends on income, goals, and future tax rates.
Conclusion
The tax deferred meaning is simple once you break it down: taxes are postponed, not avoided. This strategy can help money grow and ease financial pressure today, but it requires planning for future tax payments.
Knowing how tax deferral works allows you to make smarter decisions about savings, investments, and retirement.